Model approximation¶
Note that these potential functions only approximately represent molecular structures.
For example, bond vibrations are commonly represented as a simple harmonic with a force constant and bond equilibrium length that represent the characteristics of the bond. Such a representation is not realistic because it renders the bond as unbreakable, as shown in the diagram below.
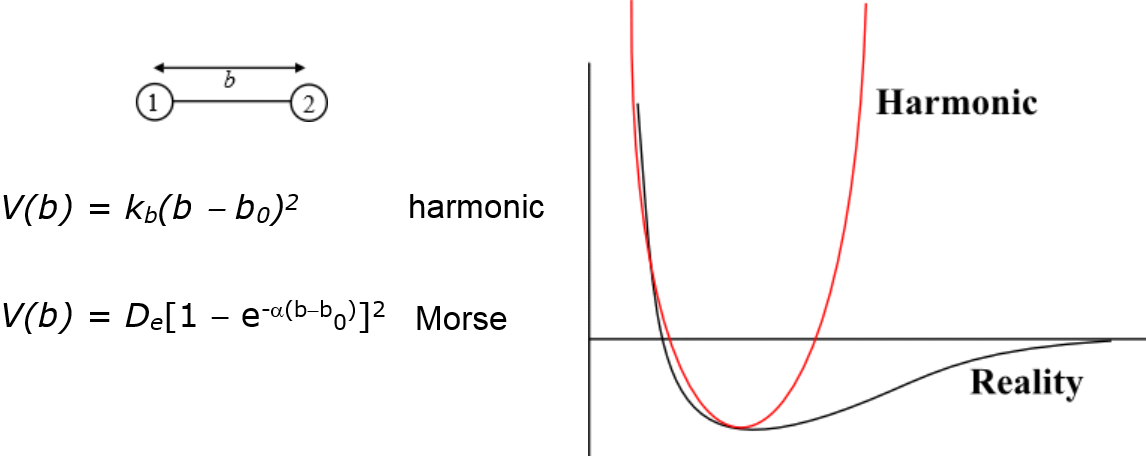
Note that the harmonic function is only a close fit around the equilibrium distance \(b_0\). This approximation is usually applicable close to room temperature (298 K) and might not be appropriate for higher temperatures.
Alternatively, a Morse function, which provides a better fit to reality, can be used. It is a better approximation for the vibrational structure of the molecule that accounts for the anharmonicity of a real bond.
The Morse function would need fitting to three parameters:
- \(D_e\), the well depth, which measures the bond strength
- \(\alpha\), which is associated with the width of the potential
- \(b_0\), the equilibrium bond length
The quantity \(\alpha\) is related to the (harmonic) force constant, \(k_b\), at the minimum well depth: