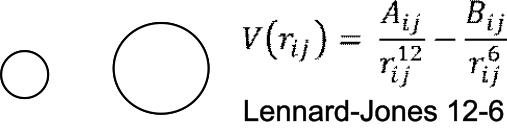Potential functions¶
As mentioned earlier, all interaction components are represented by some mathematical functional forms. While the precise functions and their implementations depend on the FF schemes, the force field model or the total energy of the system generally can be expressed as follows:
where

Below is a list of typical functional forms representing a range of interaction components.
Bond interaction, \(V_{bond}\)
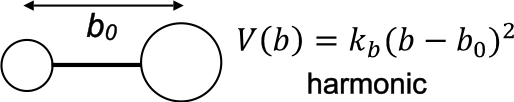
where \(b_0\) represents the equilibrium bond length and \(b\) is the bond distance (at a given moment during the MD simulation).
Angle interaction, \(V_{angle}\)
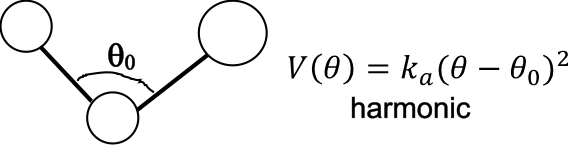
where \(\theta_0\) represents the equilibrium angle.
Dihedral interaction, \(V_{torsion}\)
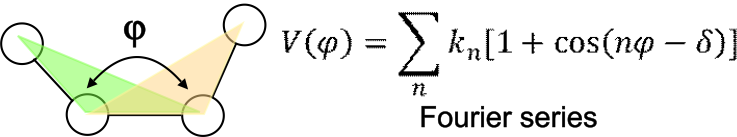
where \(k\) is the dihedral constant, or torsion barrier, \(n\) is the periodicity and \(\delta\) is the phase shift.
Cross terms, for example bond-angle, \(V_{bond, angle}\)
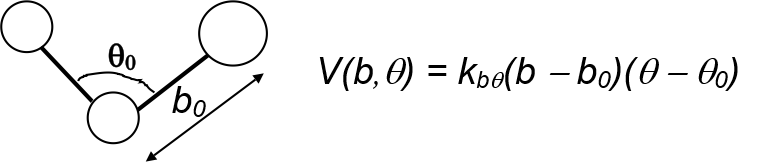
Electrostatic, \(V_{Coulombic}\)
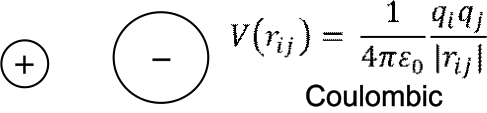
Dispersive, \(V_{vdW}\)