Atom Typing¶
The atom typing is a procedure to decide the ATOM_TYPEs of every atoms in the system. Eact ATOM_TYPE is referenced to a specific ATOM_KEY, and from such, to assign the appropriate FF parameters.
Different FF schemes use different rules to determine the ATOM_TYPEs. For this reason, converting one FF model to the other FF models is often a non-trivial task.
DL_FIELD uses the following approaches to obtain ATOM_TYPEs:
- Template matching (for PDB files).
- Molecular topology analysis using the DL_F Notation (for xyz, mol2 files).
- Combination of both (for xyz).

Template Matching
This atom typing procedure involves matching of molecular system against pre-defined MOLECULE templates in the sf files or the udff file if available. DL_FIELD will give an error if no suitable template is found.
Once a MOLECULE is identified, ATOM_TYPEs are assigned according to the connectivity information and the atoms are rearranged according to the template assignment.
In summary, template matching has the following characteristics:
- A MOLECULE template must be explicitly pre-defined, indicating the ATOMs and the corresponding ATOM_TYPEs and charges.
- Possible to use auto-CONNECT feature to simplify the template definition. Useful for complex MOLECULEs.
- Can fine tune model behaviour - introduce constrains, rigid body, core-shell and pseudo-points.
- Useful for specific classes of molecules - proteins (amino acid residues), DNA and carbohydrates.
- Suitable for user’s structures in PDB, with a correct MOLECULE_KEY.
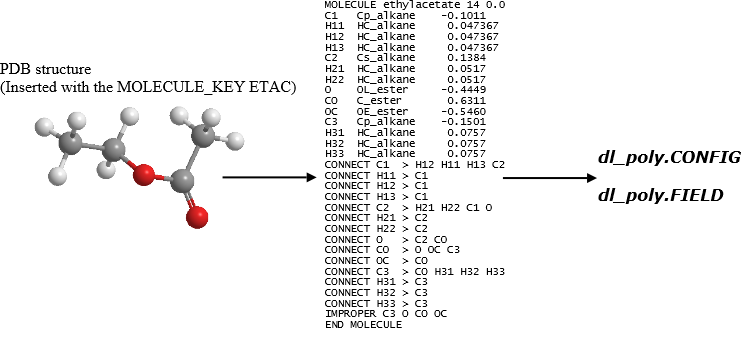
The disadvantage of using template matching procedure is that the MOLECULE template construction can be tedious and the ATOM_TYPEs must be pre-assigned by the users.
Diagram above illustrates the FF conversion of ethyl acetate (ethyl ethanoate) for Amber GAFF force field. In the PDB file, the MOLECULE_KEY ETAC must be inserted in the PDB file. DL_FIELD will base on this information to look for the corresponding MOLECULE template to produce the DL_POLY FF files.

Molecular topology analysis
Carry out detailed molecular topology analysis. From such, DL_FIELD can determine the chemical nature of every atom in the system that naturally expresses by the ATOM_TYPEs, by making use of the DL_F Notation (see next page).
In summary, the topology analysis approach has the following characteristics:
- Do not need to create MOLECULE template.
- Do not need to decide ATOM_TYPEs. This is done automatically by DL_FIELD (auto atom typing).
- Limited fine-tuning options. For example, only allow constrains on H-containing bonds.
- Applicable to OPLS2005, PCFF and CVFF only.

Combination of both procedures
Some FF schemes require the use of templates to setup FF models. CHARMM and AMBER are two of such examples and they are called the template-based FF. Normally, PDB files would be needed. However, DL_FIELD allows the use of xyz file, provided the MOLECULE templates are available, either in the .sf file or the udff file.
In the case, DL_FIELD will automatically identify the molecules in the system and search for a suitable template to match with the molecules. Once a template is found, it will carry out the template matching procedure as mentioned above.
In summary, combined procedure has the following characteristics:
- Applicable to CHARMM, AMBER and some OPLS-type FF such as CL&P and DES.
- Need pre-defined MOLECULE templates, that consists of individual small molecules.
- Does not apply to complex structures such as proteins, DNA, polysachharides, etc.